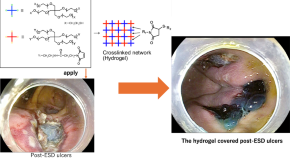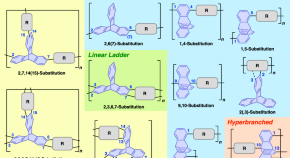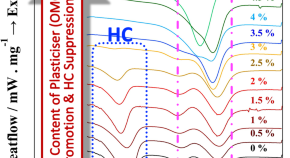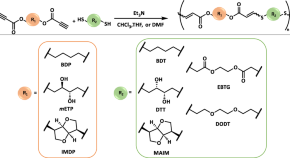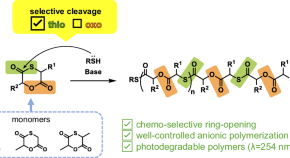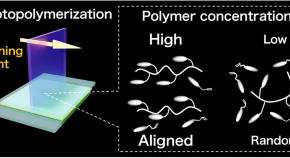
Preparation of molecularly well-defined silicone resins based on trifluoropropyl-substituted trisilanol and their thermal, mechanical, and UV-resistance properties
Free-standing films of trifluoropropyl-substituted open-cage silsesquioxane-pendant polysiloxane were prepared by optimizing sol-gel reaction condition and showed good flexibility optical transparency